Insights on green infrastructure headlines that matter
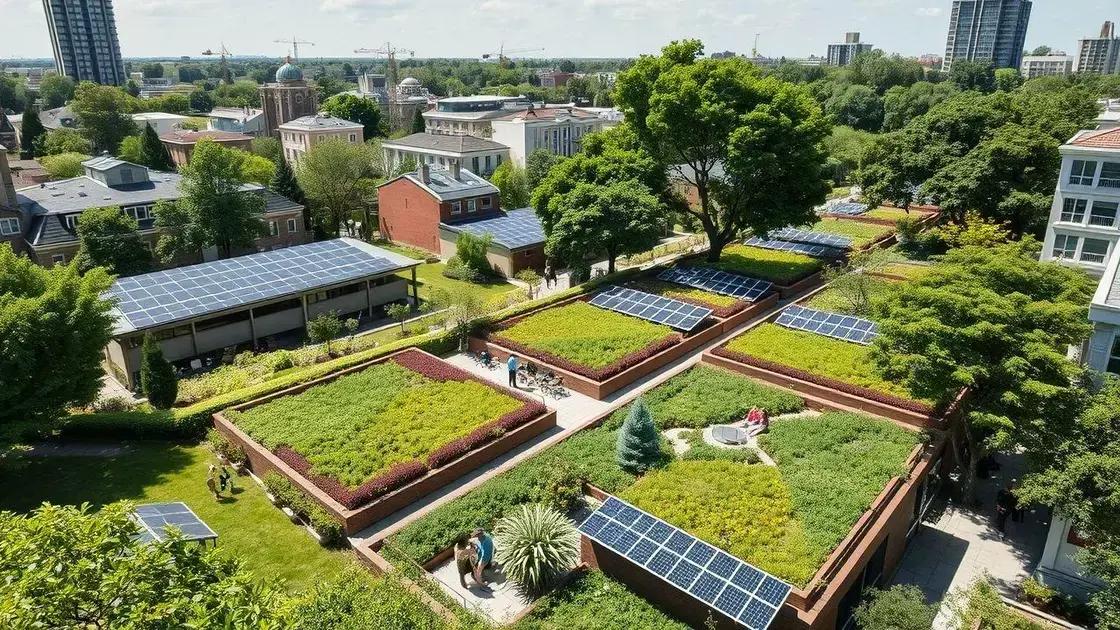

Green infrastructure enhances urban environments by managing stormwater, improving air quality, increasing biodiversity, and promoting community engagement, making cities more resilient to climate change.
Insights on green infrastructure headlines reveal how urban areas are transforming to embrace sustainability. Ever thought about how these changes affect your surroundings? In this article, we’ll dive into the essentials of green infrastructure and what it means for our cities.
Understanding green infrastructure and its benefits
Understanding green infrastructure is essential for creating sustainable urban spaces. This approach combines nature with urban planning, enhancing our cities and the environment.
Green infrastructure includes various elements such as parks, green roofs, and permeable pavements. These features help manage stormwater, improve air quality, and provide recreational spaces for communities. By incorporating nature, cities can address many environmental issues.
Benefits of Green Infrastructure
There are numerous advantages to adopting green infrastructure. Some key benefits include:
- Stormwater management: Green roofs and rain gardens absorb rainwater, reducing flooding risks.
- Improved air quality: Plants filter pollutants, leading to cleaner air.
- Enhanced biodiversity: Green spaces provide habitat for wildlife.
- Community health: Access to parks encourages outdoor activities and social interaction.
In addition to environmental improvements, green infrastructure fosters economic growth. Cities can attract tourists with beautiful parks and green areas. Furthermore, properties near green spaces often have higher values.
Moreover, using green design principles can lead to significant energy savings. For example, green roofs can insulate buildings, reducing heating and cooling costs. Ultimately, green infrastructure is more than just aesthetics—it is a solution for a sustainable future.
Examples of successful green infrastructure projects
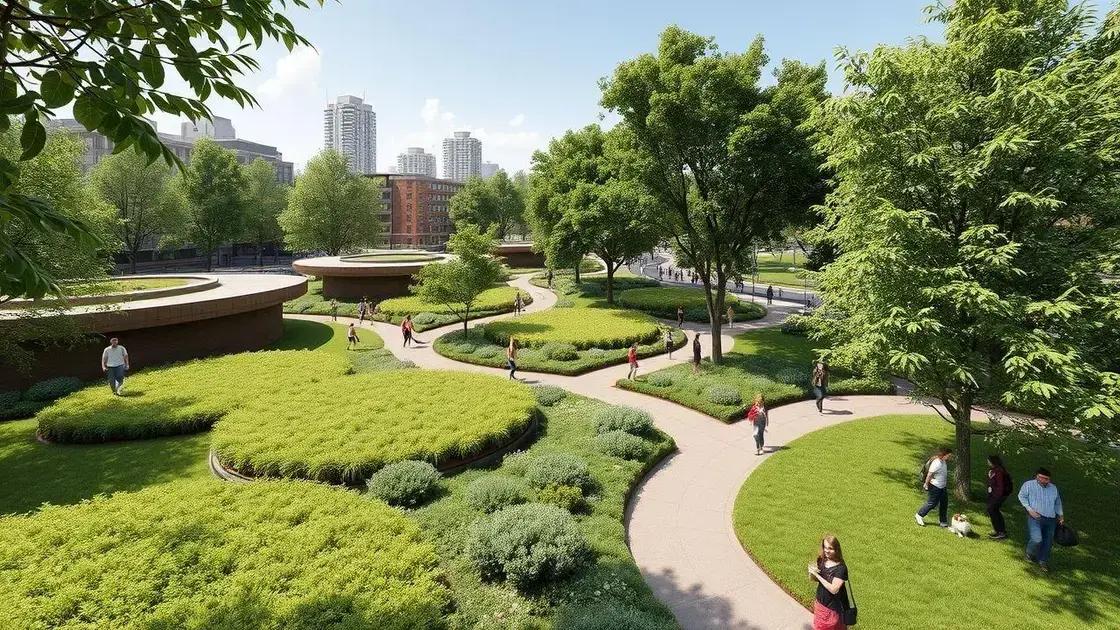

Exploring examples of successful green infrastructure projects can inspire cities to adopt similar initiatives. These projects show how blending nature with urban spaces leads to better environments and healthier communities.
One notable example is the High Line in New York City. This transformed elevated railway is now a beautiful park filled with native plants. It has improved air quality and provided a unique space for art and community events.
Another Successful Example
The Chicago Green Roofs initiative showcases how buildings can incorporate greenery. Many rooftops are now equipped with gardens that reduce heat and stormwater runoff. This not only makes the city more attractive but also helps in managing rainwater effectively.
- Stormwater management: Chicago’s green roofs absorb excess rain, minimizing flooding.
- Energy efficiency: They lower the temperature of buildings, saving energy costs.
- Biodiversity: These rooftops create habitats for various species.
Furthermore, the Toronto Waterfront Revitalization project demonstrates a holistic approach. This initiative combines parks, waterfront access, and natural landscapes. It aims to restore aquatic ecosystems and improve community spaces.
Similarly, Millennium Park in Chicago exemplifies public green space that integrates art, nature, and community activities. This park features native plants and sustainable design elements, enhancing the urban landscape.
These projects highlight effective strategies for using green infrastructure. They not only provide aesthetic value but also deliver environmental benefits, showcasing the importance of integrating nature into urban planning.
How green infrastructure impacts climate resilience
How green infrastructure impacts climate resilience is a crucial topic in today’s fight against climate change. Incorporating nature into urban planning can help cities better withstand environmental challenges.
One primary benefit of green infrastructure is its ability to manage stormwater. By using features such as rain gardens and permeable pavements, cities can significantly reduce flooding during heavy rains. This approach allows water to soak into the ground, which decreases runoff and protects water quality.
Mitigating Urban Heat Islands
Additionally, green infrastructure helps combat the urban heat island effect. This phenomenon occurs when cities become significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas. Green roofs and tree canopies provide shade and lower surface temperatures and minimize energy costs for cooling.
- Shaded areas: Reduce reliance on air conditioning.
- Increased vegetation: Helps cool the air through evapotranspiration.
- Improved air quality: Green spaces minimize air pollution effects.
Moreover, green infrastructure enhances biodiversity, which is essential for a resilient ecosystem. Diverse plant and animal species contribute to healthy habitats that can adapt over time. This diversity fosters natural systems that can withstand stress from climate impacts.
By integrating green solutions, cities not only enhance their beauty but also improve the quality of life for residents. Access to green spaces encourages active lifestyles, which is vital for community well-being in a changing climate. Furthermore, these infrastructures could serve as natural barriers against extreme weather events.
Future trends in green infrastructure implementation
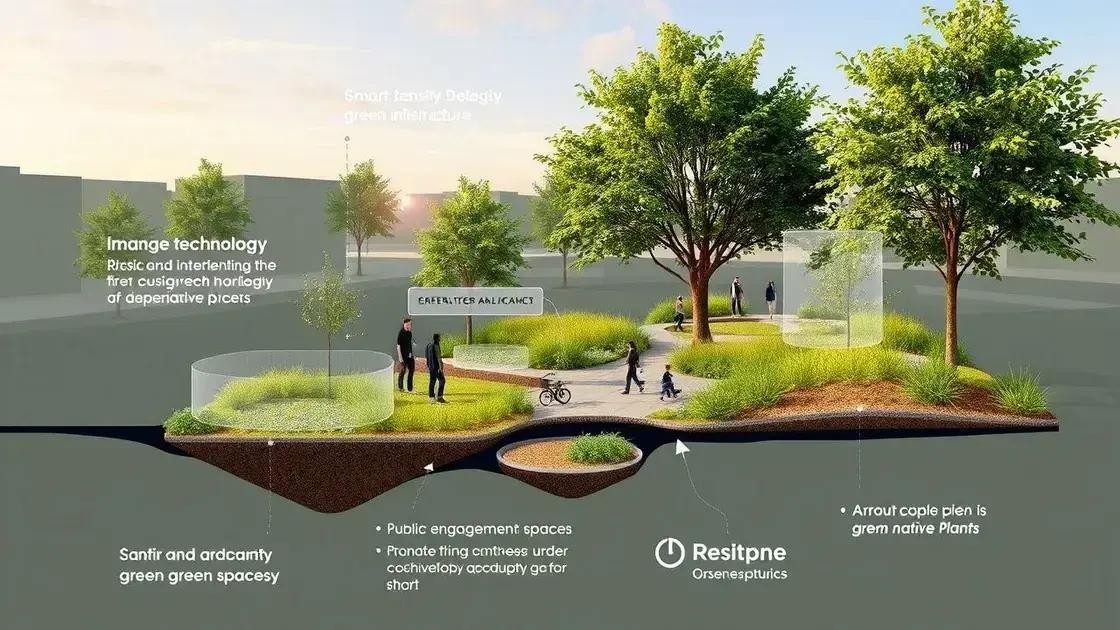
Future trends in green infrastructure implementation are shaping how cities adapt to climate change and improve urban living. Innovations in design and technology are essential for sustainable development.
One significant trend is the integration of smart technology into green infrastructure. This includes using sensors to monitor water usage and environmental conditions. By collecting real-time data, cities can manage resources more efficiently and respond swiftly to changes.
Green Infrastructure as a Service
Additionally, the concept of green infrastructure as a service is gaining traction. This model allows cities to collaborate with private firms to implement green solutions. By outsourcing these services, urban areas can leverage expertise and reduce costs while enhancing sustainability.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reduces initial investment for cities.
- Expertise: Leverages knowledge from specialized firms.
- Flexibility: Allows cities to adapt projects based on changing needs.
An emerging focus on public engagement also plays a crucial role. Communities are increasingly involved in designing and maintaining green spaces. This collaboration fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to local environments.
Moreover, the use of native plants in urban landscaping continues to gain popularity. These plants require less water and maintenance, making them ideal for sustainable design. Incorporating native species also supports local wildlife, contributing to biodiversity.
Another trend is the emphasis on multi-functional spaces. Urban designers are creating areas that serve multiple purposes, such as parks that also manage stormwater. These spaces provide recreational opportunities while addressing environmental challenges.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Green Infrastructure
What are the main benefits of green infrastructure?
Green infrastructure provides multiple benefits including improved air quality, enhanced climate resilience, and increased biodiversity.
How does green infrastructure help manage stormwater?
Features like rain gardens and permeable pavements allow water to soak into the ground, reducing flooding and improving water quality.
Why is community engagement important in green infrastructure projects?
Involving the community fosters a sense of ownership and commitment, ensuring the spaces meet local needs and preferences.
What trends are shaping the future of green infrastructure?
Trends include the integration of smart technology, public engagement, and the use of native plants to enhance sustainability.






